What is Kubernetes(K8s)? Kubernetes is an open source container-orchestration framework which was developed by Google in 2014. It helps in managing containerized applications in different environments.
Why do we use Kubernetes?
Kubernetes has no downtime so it's always accessible to the users. It also restarts containers that fail, replaces containers, kills containers that don't respond to your user-defined health check. Kubernetes scale your applications fast when you have more load on it and more users are trying to access it.
Kubernetes Architecture
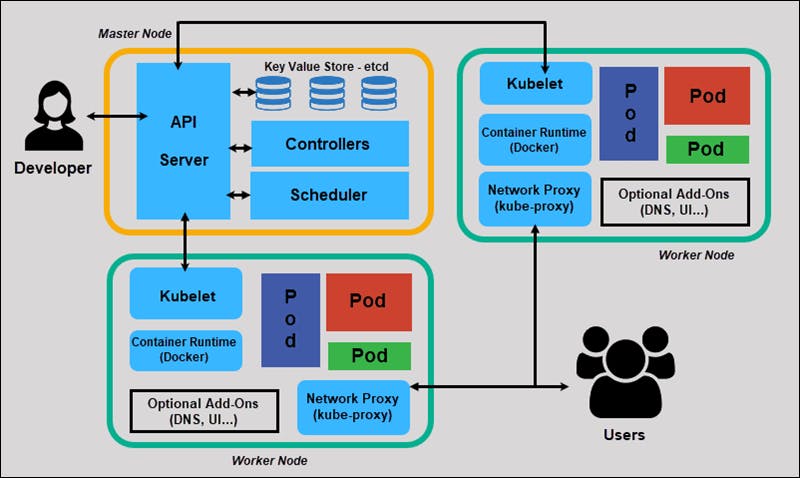 Kubernetes when started gives something called a cluster which consists of control plane and worker nodes. These worker nodes are the ones that run containerized applications. Every cluster has at least one worker node.
Kubernetes when started gives something called a cluster which consists of control plane and worker nodes. These worker nodes are the ones that run containerized applications. Every cluster has at least one worker node.
Control Plane
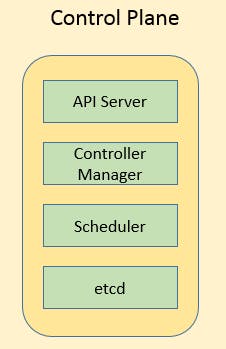 It is a collection of various components that help us in managing the overall health of the cluster. The control plane's components make global decisions about the cluster
as well as detecting and responding to cluster events.
It is a collection of various components that help us in managing the overall health of the cluster. The control plane's components make global decisions about the cluster
as well as detecting and responding to cluster events.
Control Plane Components :-
API server
When a person need to install a brand new utility in a Kubernetes cluster the person interacts with the API server with the help of a client. All the communication occurs through it. Kubectl talks to the API server to carry out any operations.
Scheduler
You send the API server a request to schedule a brand new pod, the API server after it validates your request will hand it over to the scheduler. Scheduler instead of randomly assigning it to any node first looks at how many resources application requires and according to that assigns it.
Control Manager
It detects crashing of pods. So while pods die controller manager detects that and attempts to get better the cluster state as quickly as possible and for that it makes a request for the scheduler to reschedule the restart of that pod.
etcd
etcd which is a key value store of a cluster state. It is a like the brain of the cluster. Every change in the cluster gets saved or updated into this key value store of etcd. The scheduler gets the information like what resources are available on each worker node and the controller manager knows that a cluster state changed in some way through etcd.
Worker Node
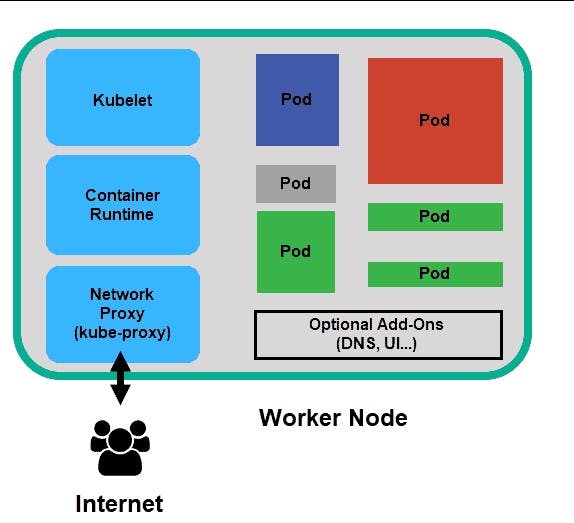 It is the environment where the application runs. It is managed by control plane. It has 3 main components which are described below :-
It is the environment where the application runs. It is managed by control plane. It has 3 main components which are described below :-
Components of the Worker Node:-
Kubelet
It runs on each node in the cluster. It's number one goal is that it looks at the specification of the pods entered into the API server and makes sure that the containers described in that pod specification are running and healthy. It restarts the pod if any issue is noticed by it.
Kube-Proxy
It is a network proxy that runs on each node in your cluster. It maintains the entire communication through networking. If worker node or cluster wants to communicate with outside network it makes sure to provide a communication medium. It also provides every worker node to have its own unique IP address.
Container Runtime
It is responsible for running containers. A container runtime is required on every node in your cluster. Without it, pods in Kubernetes are non-existent.
Kubernetes DNS
Kubernetes has its own internal DNS service. Every cluster has its own IP address and K8's DNS makes sure communication between different pods in separate cluster is possible.
Thank you all for giving your valuable time for reading.
Resources :-
Kunal Kushwaha's youtube tutorials.
TechWorld with Nana's Youtube tutorials.
Any feedback or remarks will be highly appreciated.
