Table of contents
What is Docker?
Docker is a platform that helps us to build, test and containerize our applications. The container includes the application and all the dependencies required to run your application in any environment. Docker uses a client – server architecture.
Why do we need Docker?
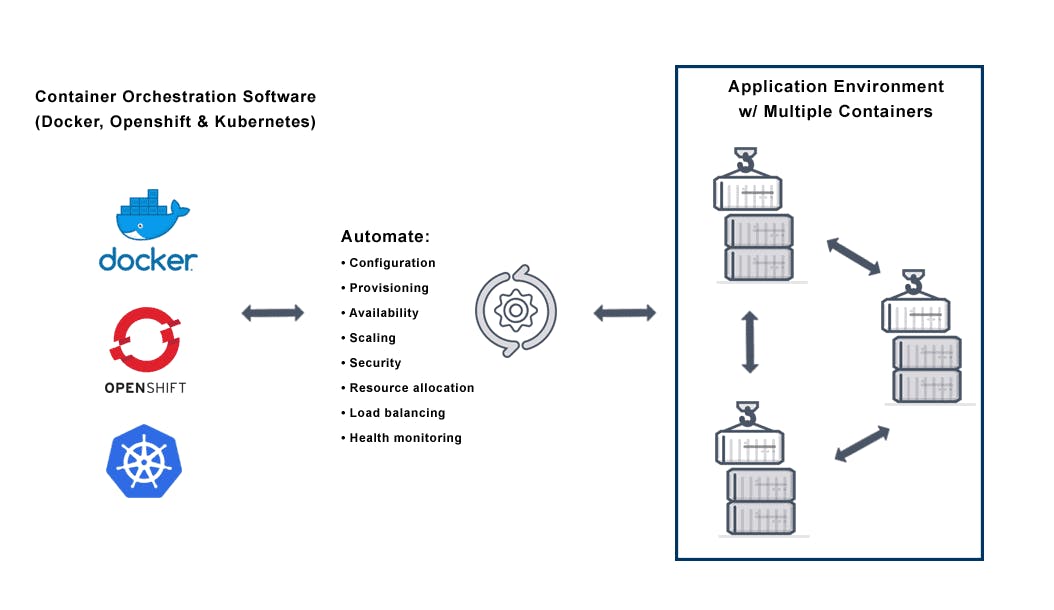 Docker helps developers to work in an isolated environment using containers without the need downloading all the dependencies. It also helps to transport code faster
Docker helps developers to work in an isolated environment using containers without the need downloading all the dependencies. It also helps to transport code faster
What is Virtualization?
Virtualization is a process in which multiple virtual environments can be created and all of them have their own guest operating system. All of these virtual environments are created on top of the host operating system. Multiple virtual machines are created with the help Hypervisor and also manages them.
What is Containerization?
Containerization is a process in which an application is encapsulated with all the dependencies and configurations required to run the application in any environment. In containerization the containers are created on top of the host operating system.
Containerization vs Virtualization
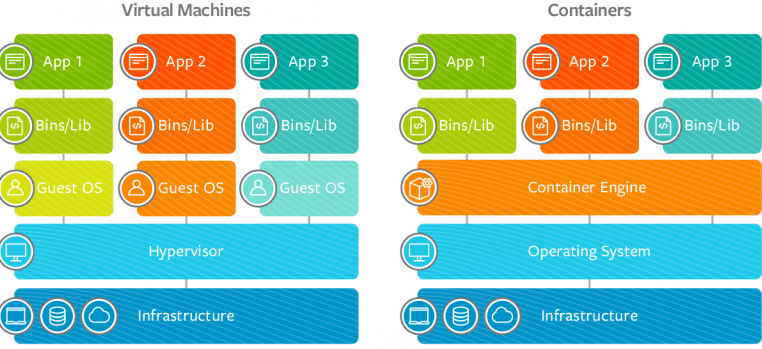
Virtualization runs on a self made operating system while containerization runs on the same operating system version as the host.
Virtualization requires more system resources such as CPU, memory, and storage whereas containerization runs on the host operating system so it requires fewer system resources.
Virtualization is hardware virtualization whereas containerization is OS virtualization.
Components of Docker

Docker Runtime
It allows us to start and stop containers. There are two types of docker runtime:
(i) Run c= Its a low-level runtime. It works with the OS to start and stop the containers.
(ii) Container d= Its a high-level runtime. It manages run c and also helps in managing containers. It also helps in pulling of images.
Docker CLI
It allows users to make commands to the Docker Daemon.
Docker Engine
It is something we use to interact with of Docker. It three components:
(i) Server – which runs the daemon.
(ii) Rest API – deals with the interaction of applications with their server.
(iii) Client – which is nothing but the command line interface (CLI).
Docker Architecture:-
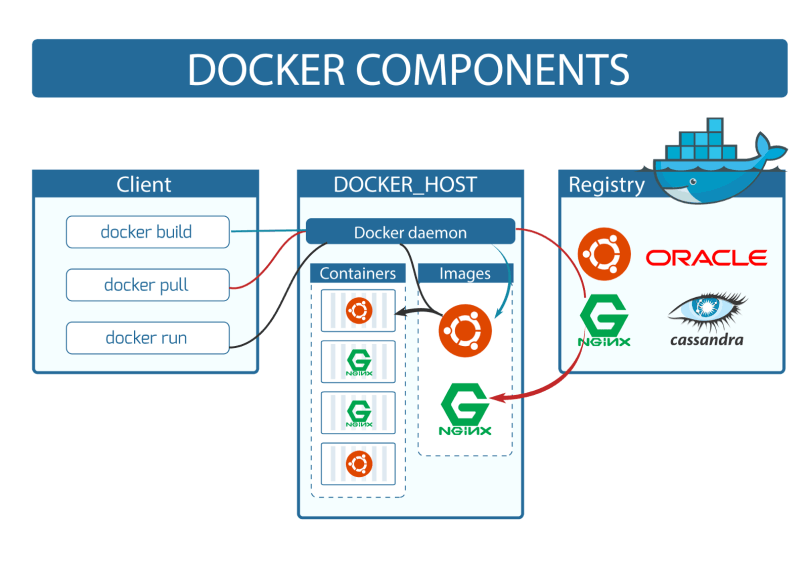
Docker Daemon:-
The API request made by Docker Client is listened by Docker Daemon and it will then build an image based on clients inputs and save it in the Registry. If the image is found not found in the local repository it downloads it DockerHub. Not only this but Docker Daemon also manages the images and containers.
Docker Client:-
Docker Client is what a user uses to interact with Docker. When a command is entered using docker, the command is then sent to Docker Daemon by Docker Client and then it is processed and carried out.
Docker Registries:-
Docker Registries is the place where images are stored. DockerHub is a public registry that anyone can use. When you pull an image, Docker by default looks for it in the public registry and saves the image on your local system on DOCKER_HOST. You can also store images on your local machine or push them to the public registry.
Images
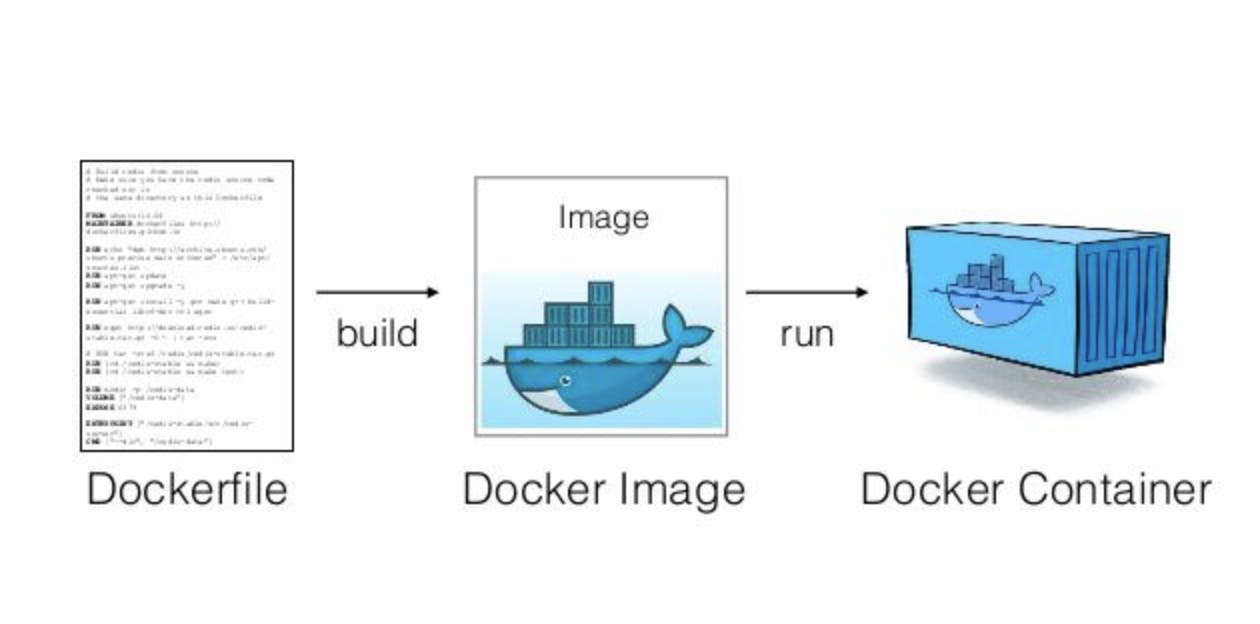 It is a file that comprises all the instructions for creating a docker container. When an image is run a container is created. The image file also contains all the dependencies required for the Docker container to run in any environment.
Images are downloaded in layers. Each layer is an immutable file which consists of files
and directories.
It is a file that comprises all the instructions for creating a docker container. When an image is run a container is created. The image file also contains all the dependencies required for the Docker container to run in any environment.
Images are downloaded in layers. Each layer is an immutable file which consists of files
and directories.
Containers
A container is a runnable instance of an image. You can create, start, stop, move, or delete a container using the Docker API or CLI. A container is a separate environment in which our application runs.
Thank you all for giving your valuable time for reading.
Resources :-
Kunal Kushwaha's youtube tutorials.
TechWorld with Nana's Youtube tutorials.
Any feedback or remarks will be highly appreciated.
